Brain Injury And Temperature Regulation. It has been shown that in. Signals between the brain and areas innervated below the level of injury may not be able to get past the site of injury. Although targeted temperature management TTM exerts pleiotropic effects the heterogeneity of brain injury has hindered identification of patient subsets most likely to benefit from TTM. Audit of temperature regulation in intensive care patients with traumatic brain injury and stroke in Australia and New Zealand CLARITY Traumatic Brain Injury TBI and Stroke ischaemic and haemorrhagic including aneurysmal and non-aneurysmal haemorrhage are globally the most common forms of neurologically-related disability in adults.
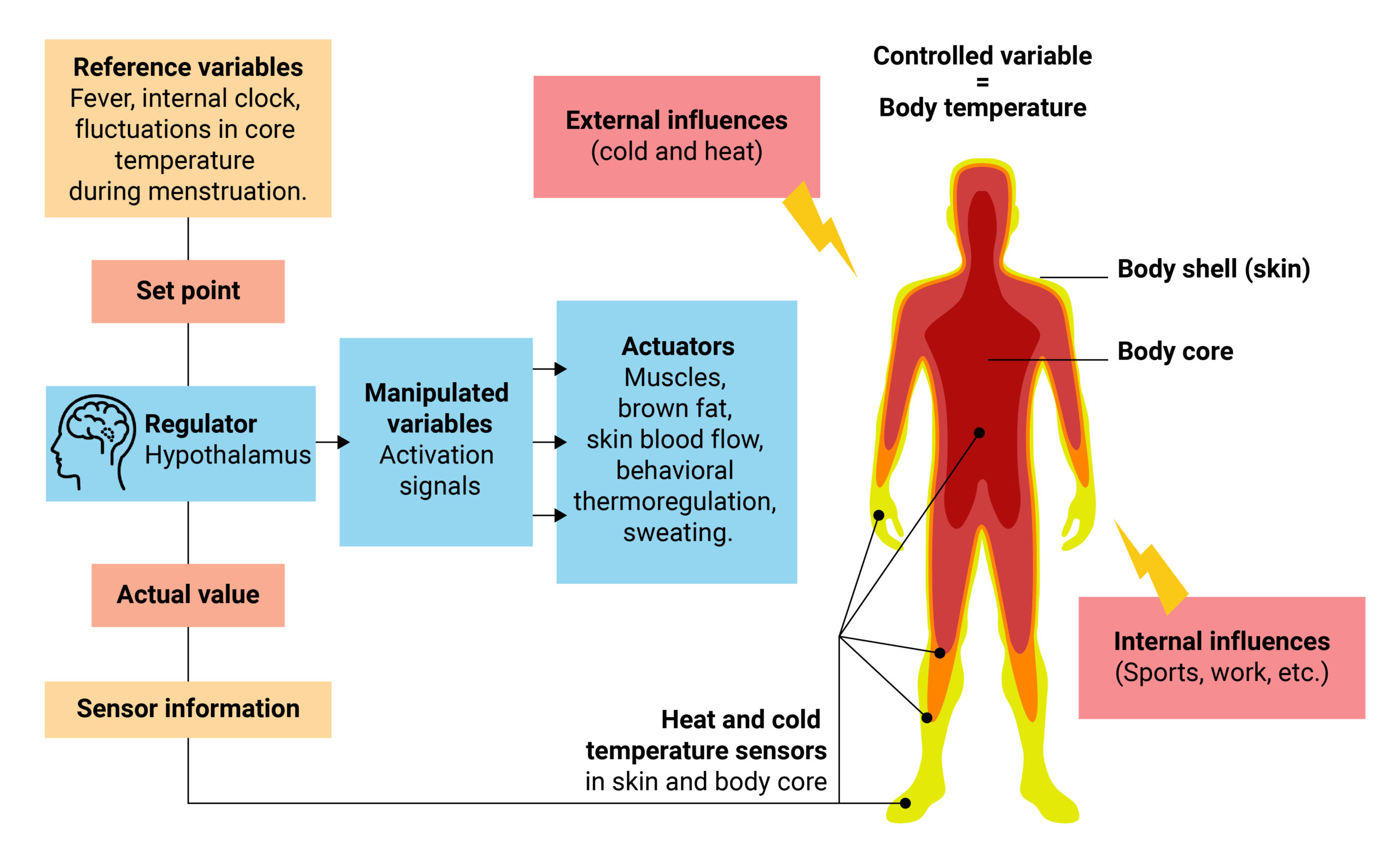
Early optimism about TTMs. The first challenge becomes determining how to measure the brains temperature as most patients are not good candidates for invasive direct brain temperature monitoring. The idea was to relax the body and mind get the heart rate rising and falling in sync with. These interactions have a great impact during brain injury and their regulation is the basis for targeted temperature management TTM in the neurocritical care unit NCCU. To mitigate the secondary brain injury in TBI patients many basic and clinical researches have been performed for the innovation of pharmacological treatments and temperature managements 3 5 7. We need to keep our body temperature around 37 C or 99 F.
This traps air next to our bodies offering some extra insulation.
While shivering during hypothermia nullifies the beneficial effect of TTM traditionally antishivering drugs or paralyzing agents have been used to reduce the shivering. Targeted temperature management TTM has been recognized to protect tissue function and positively influence neurological outcomes after brain injury. If you are in a cold place body temperature will drop. The regulation of brain temperature is largely dependent on the metabolic activity of brain tissue and remains complex. The water then evaporates from the skin and cools the body. Signals between the brain and areas innervated below the level of injury may not be able to get past the site of injury.