
Food Chain In Estuary Ecosystem. There are often three or more levels of consumers in a food chain. In a freshwater aquatic ecosystem like a pond the organisms in the food chain include algae small animals insects and their larvae small fish big fish and a fish-eating bird or animal Figure 84. Simplified feeding relationships are shown in this diagramThere are two main feeding pathways. Estuarine crocodiles do not usually consume producer ssea grasses seaweeds mushrooms and plankton in the estuary.
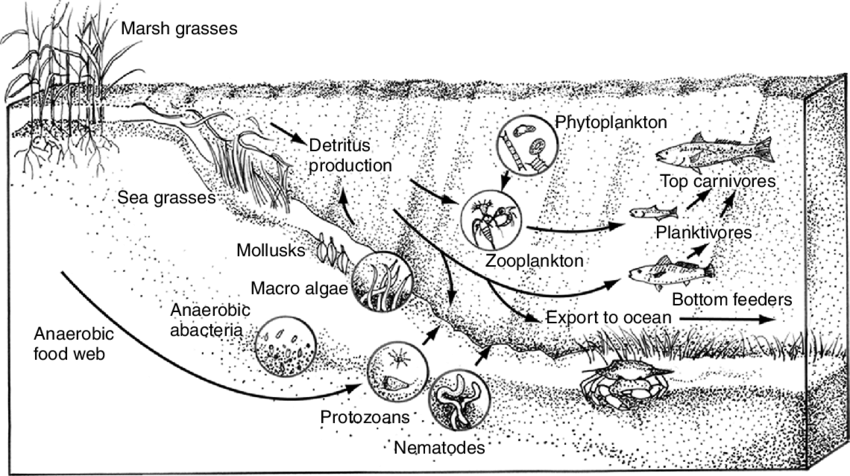
Here is a food chain of some of the organisms in the Chesapeake Bay estuary. Others like the tube worm and bristle worm also do this. There are often three or more levels of consumers in a food chain. Describe three basic trophic levels of an ecosystem. This role is mainly filled by the smaller creatures such as the burrowing crab and the snapping shrimp. Ecosystem services are the benefits people obtain from the natural environment.
In fact some of the largest and most economically important cities and fisheries are located near or within estuaries.
Produced a series ofmini-units in marine sCience education far the junior klighmiddle school classroom. This unit focuses on foodchains. Estuarine crocodiles do not usually consume producer ssea grasses seaweeds mushrooms and plankton in the estuary. Secondary tertiary and other top consumers eat primary producers and other consumers lower on the food chain. Herbivores plant-eaters come next in the chain. The food chain starts with phytoplankton converting sunlight and nutrients into living tissue.