Function Of Mitochondria In Biology. They also help in a number of cell related processes like differentiation signaling and death. Biological energy conversion in mitochondria is carried out by the membrane protein complexes of the respiratory chain and the mitochondrial ATP synthase in the inner membrane cristae. Mitochondrial function in lipid and amino acid metabolism are not discussed in this review. It is a source of energy for cellular activities.

Mitochondria function in cellular energy metabolism apoptotic pathways the β-oxidation of fatty acids in the stress response and in homeostatic regulation. Mitochondria Function of Mitochondria. The main job of mitochondria is to perform cellular respiration. Their main function is to supply the cells with ATP or adenosine triphosphate a source of chemical energy. The inner membrane is impermeable to most molecules and surrounds the vacuum containing the mitochondrial matrix. Biological functions of mitochondrial dynamics Why do mitochondria continually fuse and divide.
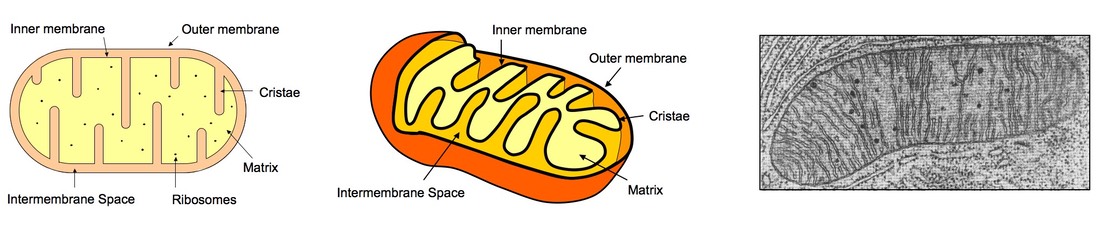
Mitochondria have two membranes an outer membrane and an inner membrane.
Alterations in mitochondrial function are increasingly recognized in cardiovascular disease. Mitochondria are a part of eukaryotic cells. ATP is high energy-rich substrates which supply 95 energy to the cell. Alterations in mitochondrial function are increasingly recognized in cardiovascular disease. In the flight muscles of insects the mitochondria called sarcosomes here are intimately associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. The most important function of the mitochondria is to produce energy.