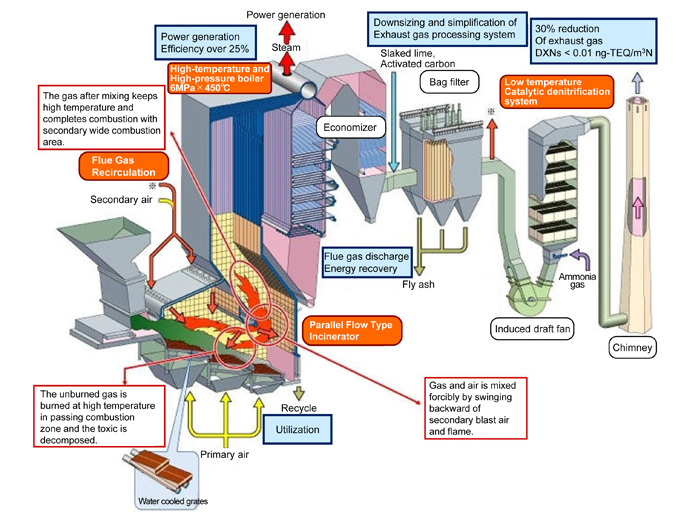
High Temperature Incineration Technology. The development of modern waste incineration technology started in the 1870s in England. Dewatered sludge will ignite at temperatures of 420 to 500C 788 to 932F in the presence of oxygen. These new technologies enabled Japans incineration plants to become safe and sound while generating electricity efficiently. Gasification is a process that converts biomass- or fossil fuel-based carbonaceous materials into gases including as the largest fractions.

Uses steam to disinfect waste commonly performed in an autoclave or other steam-based. Skip to search form. Current Land-Based Incineration Technologies A variety of technologies are used to thermally destroy hazardous wastes. 2000s 400C 2000s 300C 1990s 400C 1990s 300C 1980s 1970s Estimated Results Water cooling condenser 4MPa x 400C 3MPa x 300C. Incineration operates at temperatures sufficiently high to generate the necessary cracking and oxidation reactions to convert COCs to non-toxic combustion end. The first attempts carried out in Paddington were not successful.
Incineration is a high-temperature dry oxidation process that reduces organic and combustible waste to inorganic incombustible matter and Safe management of wastes from health-care activities.
Incineration is a high-temperature dry oxidation process that reduces organic and combustible waste to inorganic incombustible matter and Safe management of wastes from health-care activities. Skip to search form. Incineration systems are designed to volatilize and combust in the presence of oxygen halogenated and other recalcitrant organic compounds in soil and sediment that are difficult to remove at lower temperatures. Shibuya Incineration Plant is small compared to other waste treatment facilities in Tokyo and it uses a swirling flow fluidized-bed incinerator. Here the author presents an overview of this subject as a benchmark for assessment and comparison of the capabilities and performance of alternative andor developing technologies. Fluidized-bed furnaces fluidize sand layer on the floor of a tubular furnace with air to maintain high temperature which leads to efficient incineration of waste.