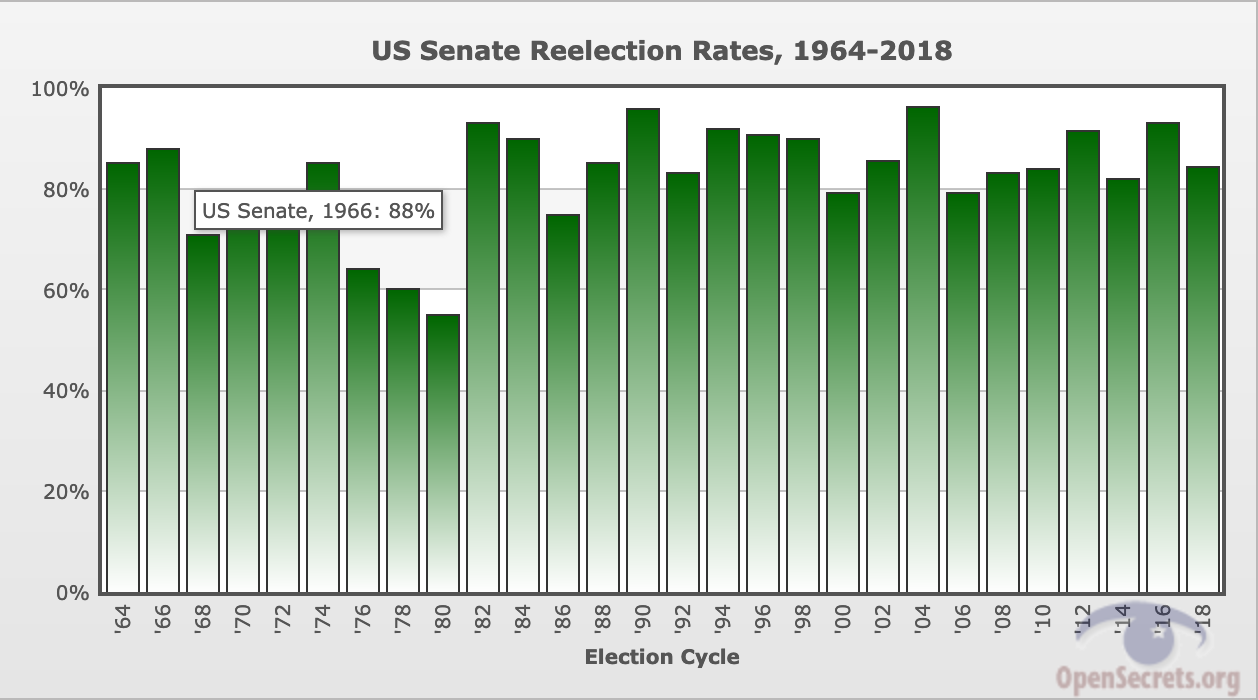
Incumbent Reelection Rate 2016. The theory has existed since the 1970s when political commentators were beginning to notice. It was 90 percent in April. The probability that an incumbent in the US. Congressional stagnation is an American political theory that attempts to explain the high rate of incumbency re-election to the United States House of Representatives.
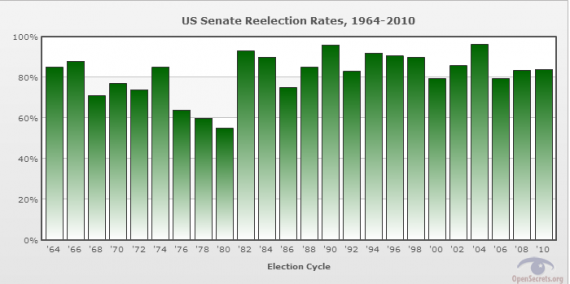
Chart 1 shows the renomination rates for incumbents seeking reelection for Senate House or governor from 1974 to the present. Levitt and Wolfram 1997 argue that decreasing challenger quality has. Less success isolating the causes of the rising incumbent reelection rate. The meme said that Congress has 11 percent approval ratings yet 964 percent of incumbent lawmakers were re-elected. House of Representatives is reelected has risen dramatically over the last half-century. Those two factors help explain why Congressional approval is at record lows but re-election rates.
House election was a better election for incumbents than 2014 and one in which the nation was split down the middle.
Incumbent reelection rates in 2016 compared with post-World. As the Center for Responsive Politics put it Few things in life are more predictable than the chances of an incumbent member of the US. The theory has existed since the 1970s when political commentators were beginning to notice. Twenty out of the 34 re-election tries were successful while 14 were not these 14 include presidents who sought their partys nomination for re-election but failed to obtain it. Big swings in the national mood can sometimes topple long time office-holders as happened with the Reagan revolution in 1980. A number of authors and commentators claim that this rise is due to an increase in bipartisan gerrymandering in favor of.