
Knee Internal Rotation Muscles. Anatomy of the knee. Upper medial surface of the tibia. External rotation with knee flexed 30-40 degrees. All the knee flexors except for the short head of biceps femoris and the popliteus are two joint muscles ie crossing the hip and knee joint.
External rotation with knee flexed 30-40 degrees. Internal rotation with knee flexed 10 degrees. 4 The tibia must internally rotate slightly to allow for knee flexion in an open chain and the femur must externally rotate for knee flexion in a closed chain. The joint capsule of the knee joint is one of a composite nature mainly formed by muscle tendons and their expansions forming a thick ligamentous sheath around the joint. All the knee flexors except for the short head of biceps femoris and the popliteus are two joint muscles ie crossing the hip and knee joint. Of the 13 muscles measured at the knee seven were significant contributors to IE rotation.
Depending on the presentation and exercise goals you can either move and forth or you can bias the movement towards internal or external rotation.
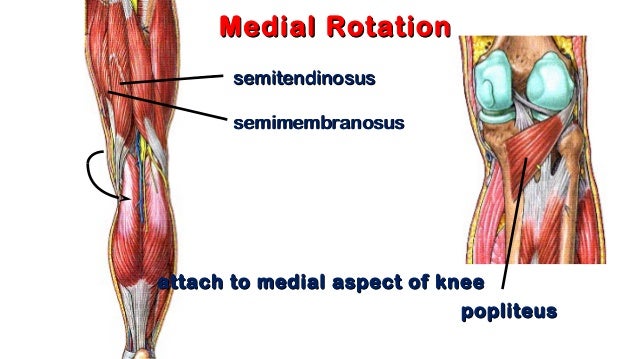
The internal rotation of your femurs is caused by short adductors short tensor fascia latae and short semitendinosis as well as short semimembranosis cf. Hamstring strains are common in individuals with chronically tight hamstrings or who do not warm-up thoroughly. These muscles include the hip abductors the external rotators the quadriceps and the hamstrings. 1 In order to unlock the knee from extension the popliteus muscle must work to initiate internal or external rotation. The biceps femoris long and short head externally rotate opposite the gracilis sartorious semimembranosis semitendonosus and popliteus functioning as internal rotators. Of the 13 muscles measured at the knee seven were significant contributors to IE rotation.