
Mcl Origin And Insertion. The median distance from the MCL femoral origin on the epiphysis to the distal femoral physis was 120 cm interquartile range 100 to 120 cm and 085 cm interquartile range 063 to 100 cm for groups A and B respectively. Posterior crucuiate ligament PCL insertion. Anterior cruciate ligament ACL origin. Prevent valgus motion of the knee or inward buckling of the knee.
- the dorsal scalenus has two muscular parts inserting on the cranial border of ribs. Its deep fibers are intimately interlaced with the joint capsule at the level of the joint and the medial meniscus is attached directly to it. The median distance from the MCL femoral origin on the epiphysis to the distal femoral physis was 120 cm interquartile range 100 to 120 cm and 085 cm interquartile range 063 to 100 cm for groups A and B respectively. Prevent valgus motion of the knee or inward buckling of the knee. The dorsally situated on the first four ribs the ventrally situated is longer and inserts on the first eight-nine ribs - the middle scalenus inserts on the cranial border of. The distal tibial attachment sites of the deep medial collateral ligament dMCL and superficial medial collateral ligament sMCL are marked with a ruler which are 1 cm and 6 cm distal to the medial joint line respectively.
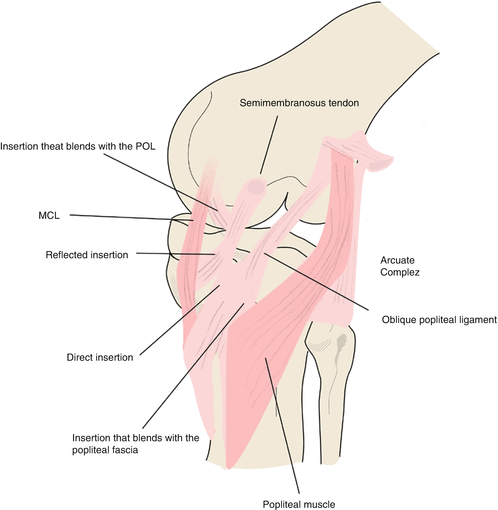
Its deep fibers are intimately interlaced with the joint capsule at the level of the joint and the medial meniscus is attached directly to it.
The ligament is composed of two layers. Medial collateral ligament Injury of the knee MCL Tear are the most common ligament injuries of the knee and are frequently associated with ACL tears. The MCL complex runs from the humerus to the ulna and is composed of three parts 1347. The femoral origin of the MCL is identified and marked. Posterior lateral side of tibia. OriginPosterior aspect of the medial gastrocnemius femoral condyle Insertion.