
Meglitinides Mechanism Of Action. Mechanisms of Action and Potential Outcomes o n Cellular. Meglitinides are oral antidiabetic drugs used especially in patients with type-2 diabetes. Because of this they are sometimes referred to as insulin secretagogues Insulin secretion is enhanced in response to a meal but does not appear to be increased during periods of fasting. It stimulates a rapid but short-lived release of insulin from pancreatic beta-cells that lasts for.
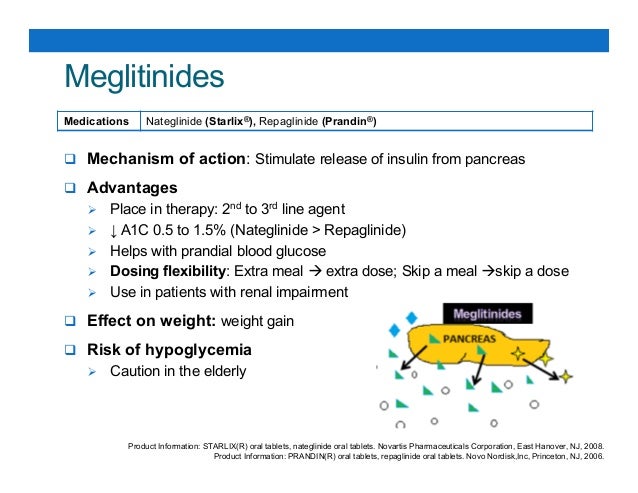
They bind to the SUR1 receptor on the β-cell although with lower affinity than sulfonylureas and stimulate insulin release in the same way. A review of Sulfonylureas and Meglitinides for Type 2 Diabetes. Meglitinides glinides are based on the sulfonylurea moiety of glibenclamide called meglitinide. They act by binding to the SUR one component of the β. Meglitinides lower blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas. Meglitinide is a benzamide belonging to the meglitinide class of antidiabetic agents with hypoglycemic activity.
Meglinitides work by stimulating the pancreas to release insulin in response to a meal.
Insulin release is glucose-dependent and diminishes at low glucose concentrations. Meglitinides glinides are based on the sulfonylurea moiety of glibenclamide called meglitinide. Meglinitides work by stimulating the pancreas to release insulin in response to a meal. Because of this they are sometimes referred to as insulin secretagogues Insulin secretion is enhanced in response to a meal but does not appear to be increased during periods of fasting. The meglitinides were developed to address this problem. It stimulates a rapid but short-lived release of insulin from pancreatic beta-cells that lasts for.