
Structure And Function Of Kidney And Nephron. Blood containing urea and metabolic waste products enters the kidney from the liver. A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidneys that regulates water and soluble substances in the blood by filtering the blood reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine. Each nephron is a coiled tube held together by a tough fibrous connective tissue. It also helps to the reappearance of desirable molecules back into the blood.
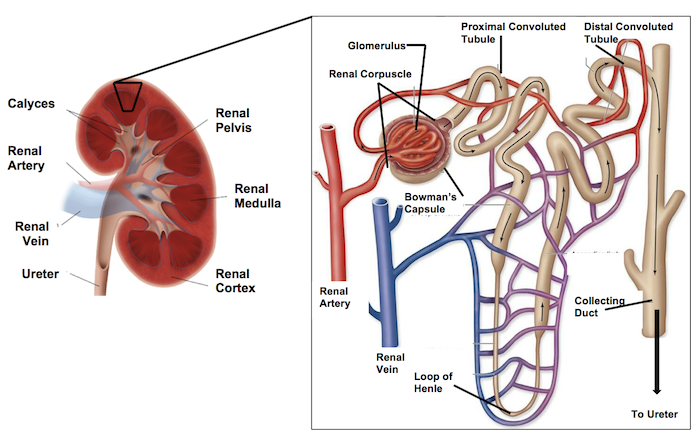
Kidney anatomy and nephron function of the renal system lecture. A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidneys that regulates water and soluble substances in the blood by filtering the blood reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine. And help to sieve or filter wastes or toxins materials from the blood and expel them outside the human body. The Functional Unit of Kidney. Lets understand in detail the structure and function of the nephron. The nephron functions through ultrafiltration.
The walls of the nephron are made of a single layer of epithelial cells.
A nephron is made up of renal corpuscles and kidney tubules or renal tubules. Nephron and its structure A nephron is the functional and structural unit of kidneys. Structure of the Nephron The kidney substance is composed of about 1 million functional units the nephrons and a smaller number of collecting tubules. Lets understand in detail the structure and function of the nephron. There are 2 types of nephrons. A nephron is made up of renal corpuscles and kidney tubules or renal tubules.