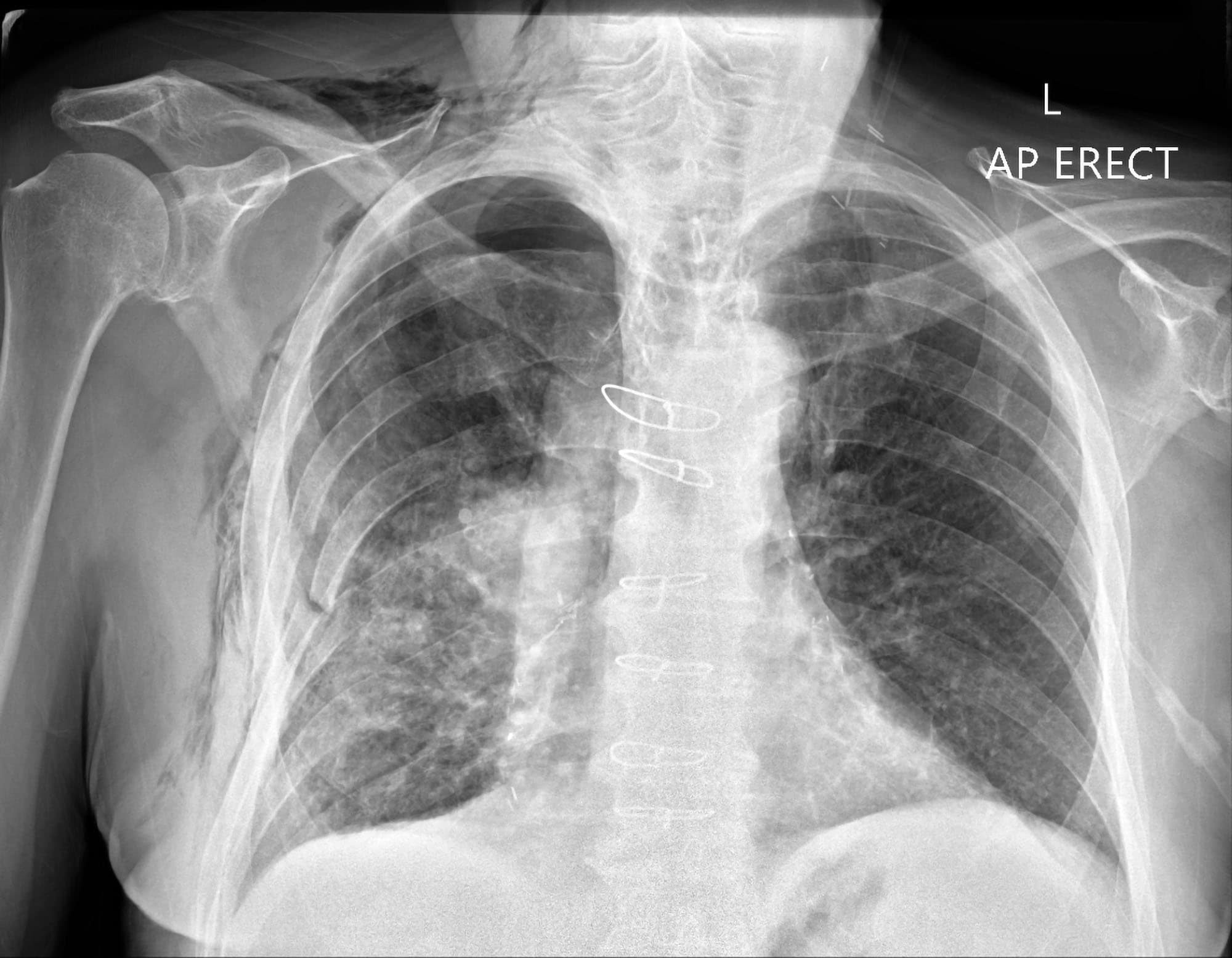
Subcutaneous Air On X Ray. On a radiograph there are intermittent areas of radiolucency often representing a fluffy appearance on the exterior borders of the thoracic and abdominal walls. Clinical conditions of relevance in anaesthesia and critical care include pneumothorax pneumomediastinum pneumopericardium pneumoperitoneum and subcutaneous emphysema. Subcutaneous air also called subcutaneous emphysema or surgical emphysema occurs in patients with chest tubes when air leaks under enough pressure to track along the tissue planes in the deepest layer of the skin the subcutaneous layer. The air comes from the chest cavity.

Other names for subcutaneous emphysema are subcutaneous air crepitus and tissue emphysema. If there are many air pockets it can make detection of a pneumothorax very difficult on a chest X-ray. In both instances the air is rather rapidly absorbed Figs. On imaging studies subcutaneous emphysema produces a striking picture of air beneath the skin surface usually covering a large area of the body The air may interdigitate with the muscle bundles to produce a characteristic linear streaky pattern especially in the. Closed traumatic injuries like contusions in which there is subcutaneous edema or hematoma may exist and appear in ultrasound as a focal area of increased echogenicity or as a nonspecific pattern of edema. This can occur at.
Chest x-ray findings associated with necrotizing fasciitis include early changes of fluid overload and adult acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS.
Subcutaneous air is visible in the left chest wall from the chest tube placement. These are of various sizes with sharply marked borders. CT may be sensitive enough to identify the source of injury causing the subcutaneous emphysema that may otherwise not be visible on an AP or lateral X-ray. Imaging including radiographic X-ray and computed tomography CT can help identify subcutaneous emphysema. Subcutaneous air also called subcutaneous emphysema or surgical emphysema occurs in patients with chest tubes when air leaks under enough pressure to track along the tissue planes in the deepest layer of the skin the subcutaneous layer. Subcutaneous air is visible in the left chest wall from the chest tube placement.