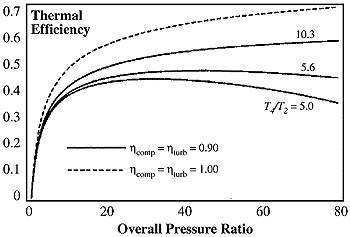
Thermal Efficiency Of Turbojet Engine. The thermal or internal efficiency of an engine is the efficiency at which it can convert fuel into kinetic energy. In a zero-bypass turbojet engine the high temperature and high pressure exhaust gas is accelerated by expansion through a propelling nozzle and produces all. Jet engines that operate with higher pressure ratios and temperatures have higher thermal efficiency. The various aspects of the SR-30 turbojet engine are discussed.

Unfortunately this temperature is limited by the thermal and mechanical stresses that can be tolerated by the turbine. Thermal Efficiency of a Turbojet Engine. This is termed as ram-compression. The inlet pressure recovery may be. Each component is instrumented with thermocouples and pressure gages to. The turbojet engine and the turbofan engine of bypass ratio 14 have the same gas generator.
Thermal Efficiency of a Turbojet Engine.
Thermal efficiency of turbojet engine calculator uses thermal_efficiency Propulsive power Fuel flow rate Calorific value of fuel to calculate the Thermal efficiency The Thermal efficiency of turbojet engine formula is defined as the ratio of propulsive power. Unfortunately this temperature is limited by the thermal and mechanical stresses that can be tolerated by the turbine. A corollary of this is that particularly in air breathing engines it is more energy efficient to accelerate a large amount of air by a small amount than it is to accelerate a small amount of air by a large amount even though the thrust is the same. The basic cycle for the turbojet engine is the joule or Brayton cycle. The thermal or internal efficiency of an engine is the efficiency at which it can convert fuel into kinetic energy. In Chapter 3 we represented a gas turbine engine using a Brayton cycle and derived expressions for efficiency and work as functions of the temperature at various points in the cycle.