
What Is A Motor Evoked Potential. The Evoked Potential testing in MS is a measurement of a set of SENSORY nerve signals. What are the risks of a sensory evoked potentials study. Transcranial electrical stimulation TCES of the brain is used to. Each of these senses trigger electrical signals in your brain.
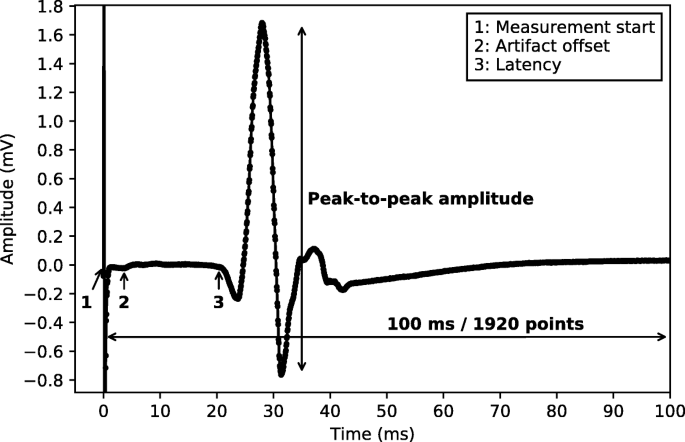
Single- or repetitive-pulse stimulation of the brain causes the spinal cord and peripheral muscles to produce neuroelectrical signals known as motor evoked potentials MEPs. An evoked potential or evoked response is an electrical potential recorded from the nervous system of a human or other animal following presentation of a stimulus as distinct from spontaneous potentials as detected by electroencephalography EEG electromyography EMG or other electrophysiologic recording method. Electrical activity is produced by stimulation of specific sensory nerve pathways. Evoked potential tests measure the time it takes for the brain to respond to sensory stimulation either through sight sound or touch. They complement other clinical neurophysiology techni-ques such as somatosensory evoked potentials SEPs in the assessment of the nervous system especially during intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring IONM. The conduction velocity is measured all the way from the origin of.
Otor evoked potentials MEPs are electrical signals recorded from neural tissue or muscle after activation of central motor pathways.
These signals are recorded and measured by electrodes attached to your body. The techniques used in these two settings differ somewhat. Each of these senses trigger electrical signals in your brain. They measure the nerve signal from a sensory organ TO the brain. They are used for intraoperative monitoring IOM and neurodiagnostic testing of the motor pathways. Relevance to actual motor behaviour.