What Is Pertussis Toxin. Clinical expression ranges from asymptomatic infection in children. The toxin appears to. The S1 component A. PT is involved in the colonization of the respiratory tract and the establishment of infection.
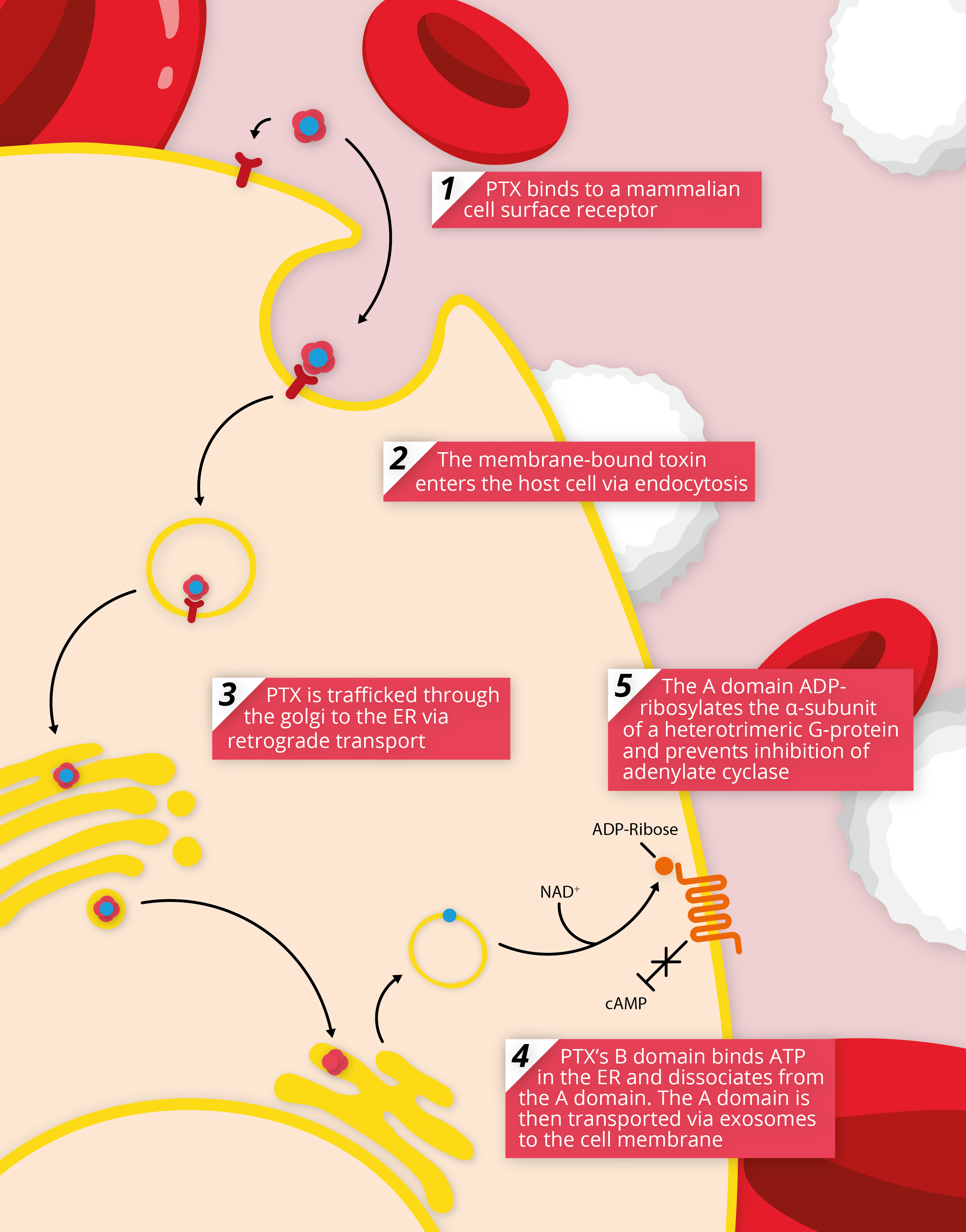
Die bindende Untereinheit lagert sich an den Rezeptor der eukaryontischen Zelle an während die funktionelle Untereinheit ein inhibitorisches G-Protein ADP-ribosyliert ADP-Ribosylierung wodurch die Inaktivierung der Adenylat-Cyclase. Bordetella pertussis a gram-negative bacterial pathogen of the human respiratory tract secretes at least two protein toxins pertussis toxin PT and adenylate cyclase toxin ACT that are important virulence factors in mouse models of infection. Pertussis toxin PT is a protein-based AB 5 -type exotoxin produced by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. PT is an oligomeric structure composed of five different subunits S1 through S5 figure 23-1. Pertussis toxinPertussis toxin subunit 1The Crystal Structure of Pertussis Toxin1IdentifiersSymbolPertussis_S1PfamPF02917InterProIPR003898SCOP1bcpSUPERFAMILY1bcp. Structurally it belongs to the A-B class of bacterial toxins.
The clinical spectrum is diverse and is affected by patient age previous exposure to the organism immunisation history antibiotic administration and concomitant infections with other agents.
Whole-cell vaccines and acellular vaccines. Pertussis toxin previously termed lymphocytosis-promoting factor is a major contributor to the pathogenesis of pertussis and is generally believed to play an important role in the induction of clinical immunity. Pertussis toxin PT is a protein-based AB 5 -type exotoxin produced by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. During a bacterial infection the toxin is secreted and causes inflammation of the respiratory tract which interferes with the clearing of pulmonary secretions. Pertussis cell envelope by the Ptl secretion system a member of the widespread type IV secretion systems. Die bindende Untereinheit lagert sich an den Rezeptor der eukaryontischen Zelle an während die funktionelle Untereinheit ein inhibitorisches G-Protein ADP-ribosyliert ADP-Ribosylierung wodurch die Inaktivierung der Adenylat-Cyclase.