
What Is Phloem And What Is Its Function. Non-photosynthetic root cells or developing flowers. Phloem tissue transports and distributes sucrose and nutrients produced by the plant during photosynthesis. The phloem is made up of living tissue which uses turgor pressure and energy in the form of ATP to actively transport sugars to the plant organs such as the fruits flowers buds and roots. Other molecules such as proteins and mRNAs are also transported throughout the plant via phloem.
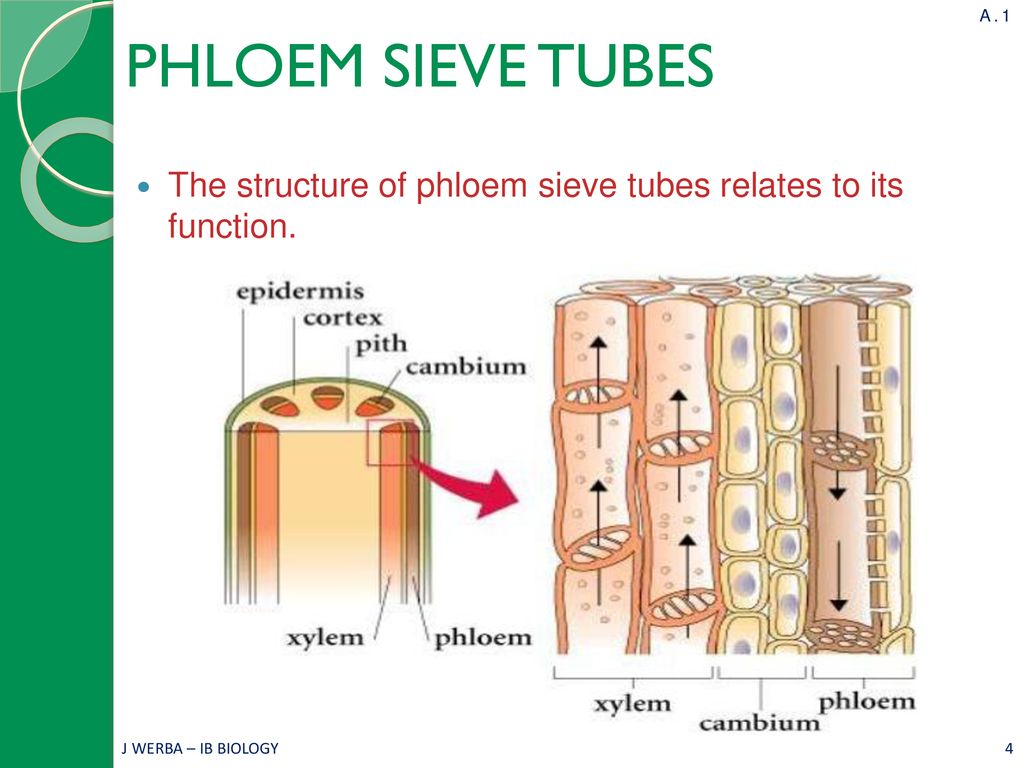
The function of the phloem tissue is to transport food nutrients such as sucrose and amino acids from the leaves and to all other cells of the plant this is called translocation. Primary phloem is formed by the apical meristems of root and shoot tips. The other material that. Functions Phloem helps in the food conductance like sugar amino acids etc. The actual tube where the sap flows is called the sieve tube and it is made up of sieve tube elements. 1 Phloem fibres with their interlocked ends form a strong strand and provide mechanical strength to the organ in which they occur.
Phloem transports food materials that are prepared by the green parts of the plants to other parts of the plant.
The sieve tubes of phloem give strength to the plant against. Phloem consists of living cells. Phloem is the complex tissue which acts as a transport system for soluble organic compounds within vascular plants. Phloem tissue transports and distributes sucrose and nutrients produced by the plant during photosynthesis. Phloem is also important as the xylem tissues for the vascular system of plants. Sieve elements parenchyma and sclerenchyma.