Tomato Plant Structure And Function. Lycopersicon and their relatives Solanum sect. 1Department of Plant and Soil Sciences University of Massachusetts Amherst Massachusetts. Tomato βgalactosidase 4 TBG4 is an enzyme responsible for fruit softening through the degradation of β14galactan in the pericarp cell wall. Schmidt a Rachel L.
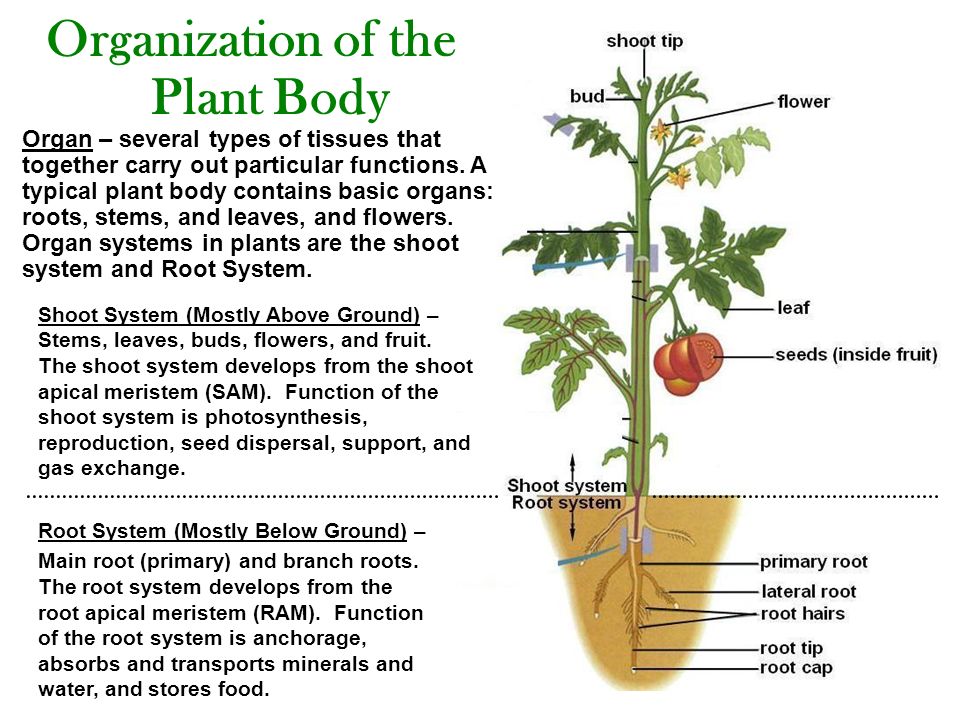
A tomatos root system fulfills three very important functions. Producing plant growth hormones. It is typically served as part of a salad or main course of a meal rather than as a dessert. Storing food for future use. Seecds were sown in flats of soil and the seedlings were grown for 5weeks in a greenhouse. The chloroplasts which are normally.
Developing new plants from the roots of the old plant vegetative reproduction.
It is typically served as part of a salad or main course of a meal rather than as a dessert. Correction for Schmidt et al Effects of Agricultural Management on Rhizosphere Microbial Structure and Function in Processing Tomato Plants - August 03 2020 ABSTRACT Given close linkages between rhizosphere processes and plant nutrition and productivity understanding how management practices impact this critical zone is of great importance to optimize plant-soil. The root system of the tomato is of pivoting type being very dense and branched on the. Anchoring and supporting the plant absorbing and conducting water and minerals to the rest of the plant and storing the products of. A plant body consisting of stems roots and leaves. A plant with fixed or indeterminate port.